Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is perhaps the most versatile of all plastic materials, satisfying an extremely wide variety of uses, ranging from life-saving medical devices to the very pipes that are the backbone of modern infrastructure. Its adaptability and low cost have caused Polyvinyl Chloride to become a go-to material for numerous industries.
However, reliance on PVC without proper familiarity with the unique demands of an application may be reflected by subpar performance, compliance problems, or lost potential with a superior material better suited to the use. This renders it essential that project managers, procurement managers, and engineers make contact with credible petrochemical distributors as well as experienced PVC raw material suppliers who can provide not only high-quality polyvinyl chloride but technical services as well. This article offers a balanced, analytical overview of Polyvinyl Chloride strengths and weaknesses to enable well-informed decisions that achieve maximum cost, performance, and durability.
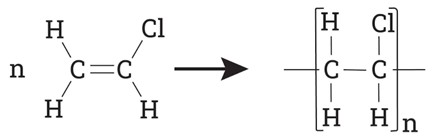
The Case for PVC: Why It Remains an Industry Staple
- Unmatched Cost-Efficiency: Among the key reasons PVC still maintains its number one position in the plastics sector is that it is extremely cost-effective. Polyvinyl Chloride raw materials are cheaper than other polymers and traditional materials such as concrete or metals due to optimized production processes and economies of scale. It's lightweight, also significantly reduces transportation and installation costs, making it a top choice for large construction and manufacturing projects. Procurement managers prefer to remain loyal to established petrochemical distributors for a steady supply of good-quality polyvinyl chloride that allows for the maximization of budgets without compromising on quality.
- Exceptional Durability and Chemical Resistance: PVC is renowned for its durability and resistance to degradation. Its inherent chemical stability renders it resistant to acids, bases, salts, and other corrosive substances that normally attack industrial and building materials. The durability is converted into extended service life and reduced maintenance, factors of essence to project managers, determined by lifecycle cost savings. Corrosion and abrasion resistance ensure Polyvinyl Chloride functionality and safety under challenging conditions, securing its role as a reliable material sourced from reputable Polyvinyl Chloride raw materials suppliers.
- Ultimate Versatility: Another attribute of PVC is flexibility. It can be designed into rigid structures (uPVC) that are used extensively in piping, window frames, and profiles, or into flexible varieties that are well adapted for tubing, sheeting, and insulation. Its versatility even extends to its application to various processes of fabrication, such as extrusion, injection molding, and calendaring, where designers and engineers can specify solutions to fit exactly to the needs of an application. By working together with qualified suppliers and well-established petrochemical distributors, companies can have access to dedicated polyvinyl chloride grades with strict performance standards applicable to several industrial uses.

The Other Side of the Coin: Acknowledging PVC's Limitations
While PVC is, in general, extremely prized for its versatility and low cost, it is worth noting for engineers and procurement managers to look at its shortcomings independently of their merits before committing to use it. One of the reasons relates to environmental and health matters: it contains chlorine, and flexible products require plasticizers such as phthalates, which have driven regulatory and health interest. It also releases toxic dioxins in uncontrolled burns, posing environmental risks.
Thermally, PVC possesses a lower ceiling to its resistance compared to other choices like CPVC or metals, i.e., its use in high-temperature applications is limited. It won't be useful for processes or installations where continuous or extended exposure to elevated temperatures is needed. Recyclability is also a problem. The density and chlorine content in Polyvinyl Chloride complicate recycling, especially when mixed with other plastics. Different additives also make it easy to recycle since they require reliance on dedicated streams of processing, typically brokered by trusted petrochemical distributors. For ease of access to grades that minimize such problems and enable sustainability goals, working with an established PVC raw material supplier is thus crucial.
Head-to-Head: PVC vs. Key Alternative Materials
PVC vs. Polyolefins (HDPE & PP):
HDPE is favored for applications needing flexibility and high impact strength at low temperatures, such as potable water systems, since it does not contain plasticizers. PVC, however, is more rigid and has better UV resistance and thus is more appropriate for structural or outdoor applications. PP finds its merits in high-temperature applications and has superb fatigue resistance, which makes it ideal for applications like living hinges. On the other hand, Polyvinyl Chloride has better flame retardancy than PP, which is a key factor in safety-critical projects. Product designers and engineers usually depend on reliable petrochemical distributors to procure the right polyvinyl chloride or polyolefin grades based on these particular requirements.
PVC vs. CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride):
CPVC is essentially PVC with chlorination added to it, hugely enhancing its heat resistance. CPVC is therefore used for hot water piping and industrial plumbing where exposure to heat is high. The downsides are higher cost and occasionally reduced availability from raw material suppliers of Polyvinyl Chloride. Procurement managers must weigh these factors very carefully when specifying temperature-sensitive applications.
PVC vs. Metals (Steel, Copper):
Steels and copper offer unparalleled strength and thermal resistance, necessary for structure or high-temperature usage. Still, the most significant advantages of PVC are cost savings, lightweight, and corrosion resistance. These render Polyvinyl Chloride a cost-saving, durable alternative to fluid transport systems where metals would be resistant or require expensive coatings. A trusted petrochemical distributor ensures quality polyvinyl chloride materials for such applications.
PVC vs. Composites (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic - FRP):
Composites give a greater strength-to-weight ratio and better chemical resistance, but at a much more costly price. Although composites are ideally suited for specialized high-performance uses, Polyvinyl Chloride remains the cost-effective material for everyday structural and flow purposes. Procurement managers balancing budget demands with performance goals often prefer Polyvinyl Chloride from reliable PVC raw material suppliers.
Choosing the Right Material for the Job
Selecting an appropriate material - either PVC or another -is mostly based on requirements for a particular application. Engineers and procurement managers must take into account both physical and chemical properties of each potential material before finalizing material specifications in writing.
Scenario 1: Residential & Commercial Plumbing
PVC is an extremely well-suited choice for drainage, waste, and vent (DWV) and cold water distribution systems. It is low in cost, easy to install, and has inherent corrosion- and microbial growth-resistance. If properly resourced from a good PVC raw material supplier, it enjoys an extended service life with minimal maintenance. However, for hot water piping, the low thermal resistance of Polyvinyl Chloride is a menace. For these uses, copper or CPVC would have to be selected to avoid material failure from long-term high temperatures.
Scenario 2: Industrial Chemical Processing
PVC is widely used for the transfer of a wide range of acids, bases, and salts under room conditions. Its chemical stability, especially if sourced from a good petrochemical vendor, makes it a suitable material for the majority of industrial environments. However, in the presence of attacking organic solvents or high-pressure and high-temperature environments, alternative materials like polypropylene (PP), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), or lined steel are better suited since they possess higher chemical and thermal resistance.
Scenario 3: Outdoor Building Materials
PVC is well-adapted to outdoor applications like siding, window profiles, and fencing. It resists UV light stability, retains low moisture absorption, and withstands rot and insect damage, making it an excellent choice for durable outdoor use. However, where appearance or load is a primary concern in projects, materials like composites or treated wood may be an even better fit.
A Buyer’s Checklist: Key Factors for Your Final Decision
Use the following guidelines when choosing PVC or other materials to make your decision easier:
- Performance Requirements: Look into the mechanical strength, range of operating temperatures, and the working pressure of the equipment.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Look at initial material prices, the complexity of the installation, and the anticipated service life.
- Regulatory Compliance: It includes certifying that the material is within the required standards. NSF is for potable water, and RoHS for electronics.
- Sustainability Goals: Check the material's end-of-life the recyclability, and assess the environmental effect.
For technical guidance and secure supply, Shobeir Shimi trading company is an established petrochemical supplier with a track record of supplying quality products to industrial consumers. Whether you're buying traditional PVC or reviewing specialty choices, Shobeir Shimi can assist your procurement strategy with technical knowledge and stable dependability.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Choice for Long-Term Success
No better material exists for everything, but the appropriate material for an application. While PVC remains a highly versatile and economical choice, other materials like CPVC, metal, or composites may be better suited to specific performance needs. Ultimately, smart material choice is all about planning, one that prioritizes performance, cost, regulation, and sustainability. Having a consistent petrochemical distributor and competent PVC raw material supplier ensures that your decisions lead to successful long-term projects and effective operation.
 icons at the top
right corner of the subsection.
icons at the top
right corner of the subsection.